All Eukaryotic Microbial Cells Have Which of the Following Structures
Okay now mitochondria is going to be a source of energy that eukaryotic cells have in order to perform different tasks. These are modified as mitochondria and chloroplast.
They are going to have structures like the cytoplasm cell wall ribosomes.

. Most eukaryotic cells also have other membrane-bound internal structures called organelles. All eukaryotic microbial cells have which of the following structures. Bacterial cells could have any of the following appendages except.
Bacterial cells prokaryotic cells are structurally much simpler than eukaryotic cells and the two cell types are compared in Table 32. 1 a membrane-bound nucleus. C the structure and function of DNA.
Bacteria cell organelles include the following. Most bacteria are capable of independent metabolic existence and growth but species of Chlamydia and Rickettsia are obligately intracellular organisms. And 3 several rod-shaped chromosomes.
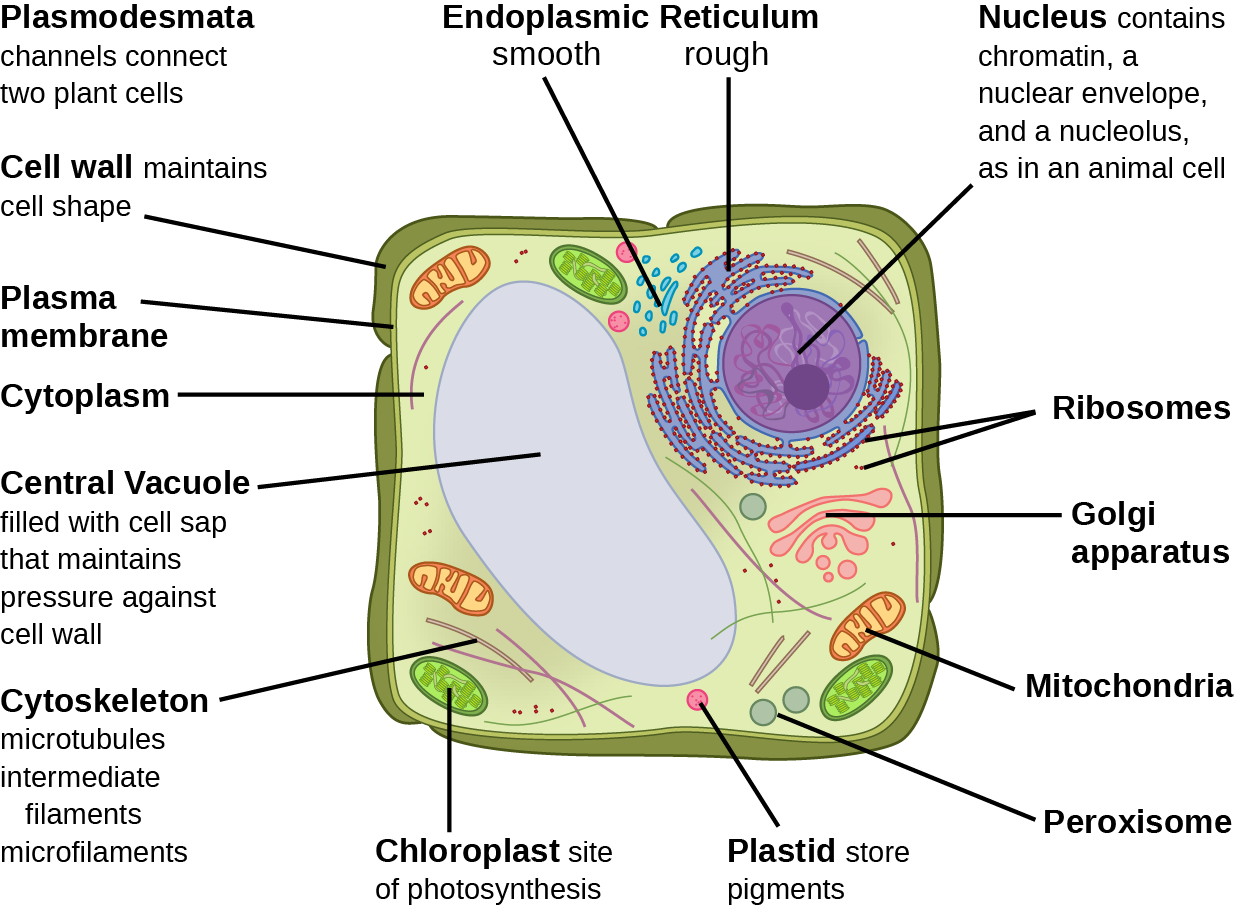
Which of the following cell structures are found in ALL Cell types. Cytoplasm including the cytoskeleton. 2 numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus chloroplasts mitochondria and others.
Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cells nucleus it has a true nucleus. P Flag question All eukaryotic cells have the following structures EXCEPT Select one. Um but one other important thing that theyre missing is mitochondria.
Like bacteria and archaea eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. All bacterial cells have. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment.
The ____________theory is used to describe the origin of some eukaryotic organelles. A thick cell wall and the cell membrane. All of the following structures contribute to the ability of pathogenic bacteria to cause disease EXCEPT the.
The cell envelope of gram-positive bacteria has two layers. C microtubular organization and type of. What is the function of eukaryotic flagella.
C protists have a membrane-bounded nucleus which bacterial cells lack. One or more chromosomes 2. Bacterial chromosomes are located in a nucleoid a distinct cytoplasmic structure in which double-stranded DNA is coated with histone-like proteins.
All eukaryotic cells have the following. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules ions water and oxygen into and out of the cell. They range in size from large.
Eukaryote have different cell organelle that performs different function this include vacoulemitochondriacell wallnucleusflagellumchloroplast. No bacteria do not have many organelles that eukaryotic cells have including the endoplasmic reticulum a nucleus and a Golgi apparatus. And 3 several rod-shaped chromosomes.
Plasma membrane Question 2 Not yet answered Marked out of 100 P Flag question In a eukaryotic cell which component is involved in both protein and lipid synthesis. Except some all structures do not occur in every genus. According to the endosymbiotic theory the bacterial cell was engulfed by an ancestral cell and concerted it into a particular organelle.
All bacteria both pathogenic and saprophytic are unicellular organisms that reproduce by binary fission. Cell membrane Glycocalyx Mitochondria Golgi. 1 a membrane-bound nucleus.
One or more chromosomes b. Because a eukaryotic cells nucleus is surrounded by a membrane it is often said to have a true nucleus. It comprises specific embedded proteins which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.
Vacoule help in storage and transportation within body system Chloroplast is the photosynthetic pigment helps trap sunlight. Which of the following is the most external structure of eukaryotic microbial cells. The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules ions water and oxygen into and out of the cell.
A cell wall is a rigid structure present outside the plant cell. Unlike prokaryotic cells eukaryotic cells have. The eukaryotic cell structure comprises the following.
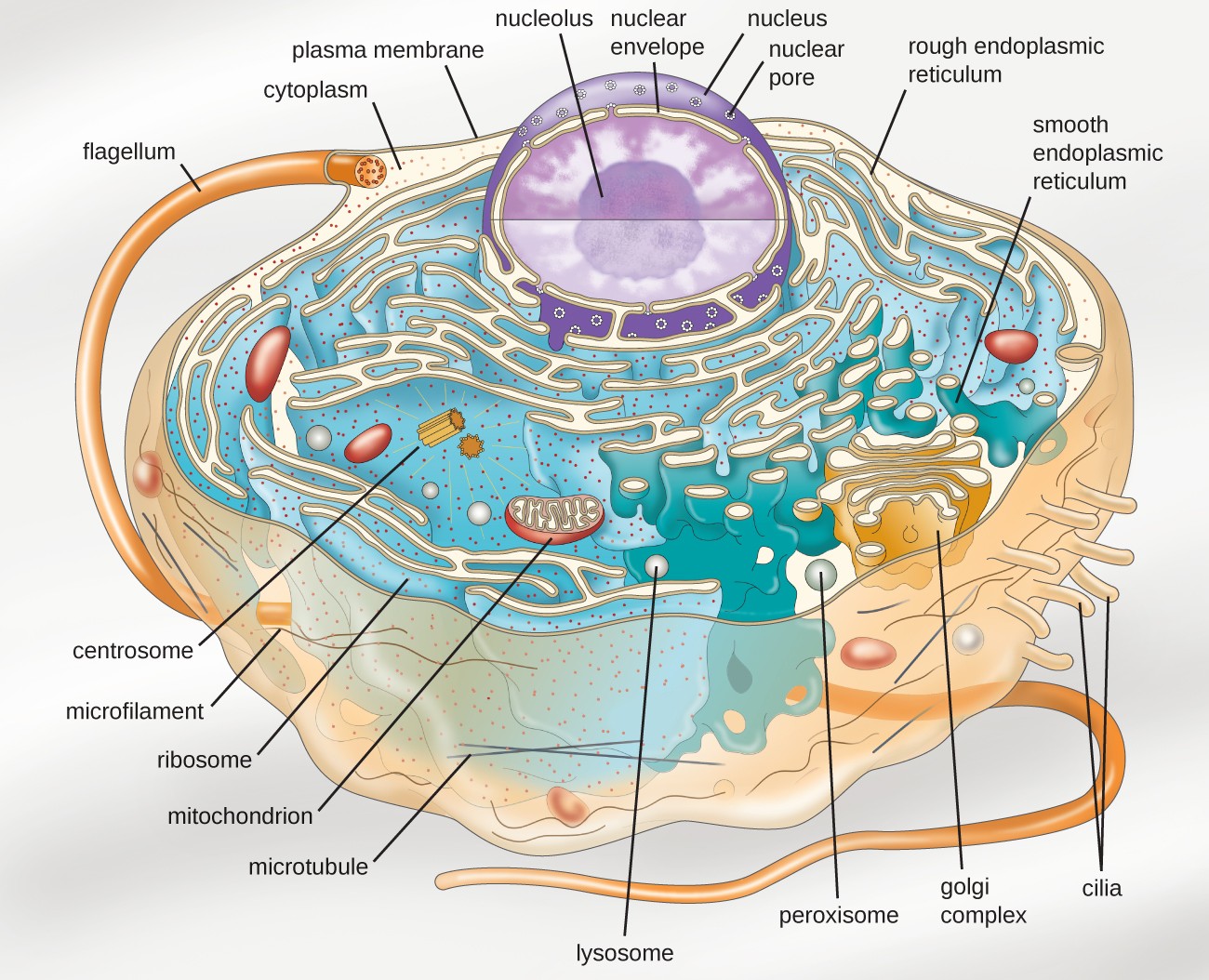
Flagella which are long flexible structures made from the protein flagellin extend out from the cell wall and give the bacterial cell added motility. Ribosomes mitochondria nucleus Golgi apparatus. You can see all those structures labeled here.
2 numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus chloroplasts mitochondria and others. Like bacteria and archaea eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. They consists of various cell surface structures cell wall plasma membrane many cytoplasmic inclusions and the bacterial chromosome nucleoid.
Most bacteria appear to have a single large circular chromosome but this is not universal. Periplasmic flagella axial filaments. A Prokaryotes characterized as extremophiles that share some bacterial and some eukaryotic traits.
Unlike prokaryotic cells eukaryotic cells have. The endosymbiotic theory supports the statement that the mitochondria includes the mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes and chloroplasts are derived from the bacteria. Describe the function of the following major eukaryotic intracellular structures.
Bacterial cells are extremely small and are most conveniently measured in microns 10-6 m. Bacterial cells have all of the following structures EXCEPT a cell wall. Compare and contrast prokaryotic bacterial cell structure with eukaryotic cell structure with respect to typical size cell boundary and presenceabsence of various intracellular compartments.

Eukaryotic Cells Definition Parts Examples And Structure

Comments
Post a Comment